- \(0\)
- \(-1\)
- \(1\)
- \(-2\)
- \(2\)
Mathematics·Studies (I)
Nat. Sciences
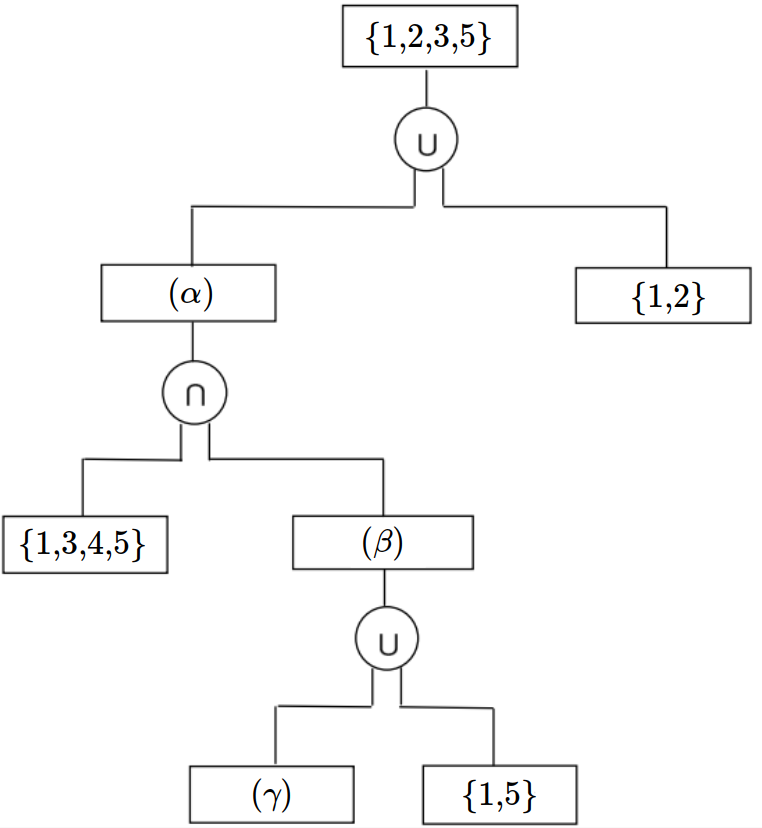
- \(\{1,2,3,4\}\)
- \(\{1,2,3,5\}\)
- \(\{2,3,5\}\)
- \(\{1,3,5\}\)
- \(\{3,5\}\)
- \(\displaystyle\int_{a+1}^{b+1}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
- \(\displaystyle\int_{2a}^{2b}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
- \(\displaystyle\int_{a^2}^{b^2}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
- \(\displaystyle\int_{\sqrt{a}}^{\sqrt{b}}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
- \(\displaystyle\int_{\,\begin{array}{c}1 \\\hline a\end{array}}^{\,\begin{array}{c}1 \\\hline b\end{array}}\,\frac{1}{x}dx\)
- \(\dfrac{3}{16}\)
- \(\dfrac{5}{16}\)
- \(\dfrac{7}{16}\)
- \(\dfrac{9}{16}\)
- \(\dfrac{11}{16}\)