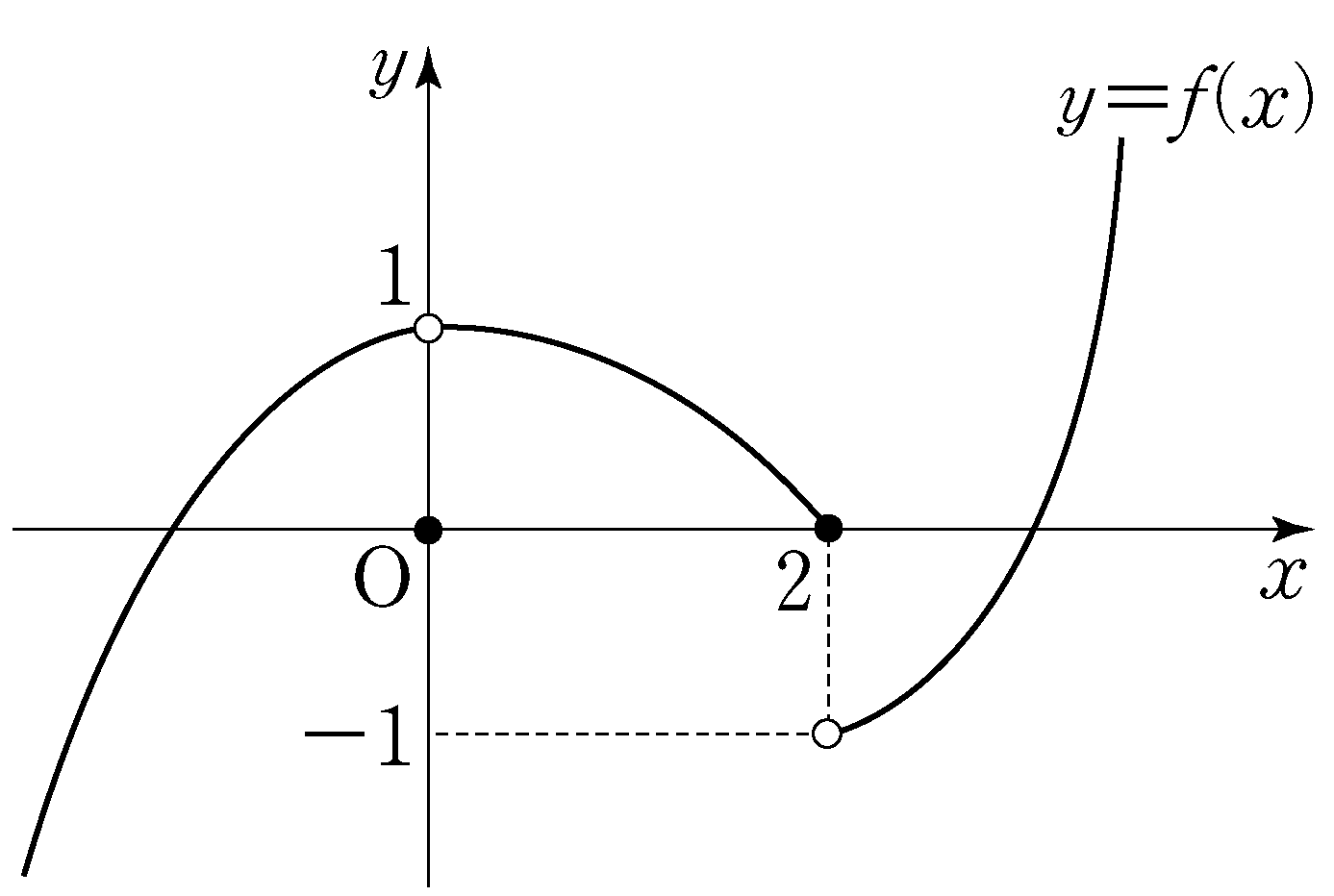
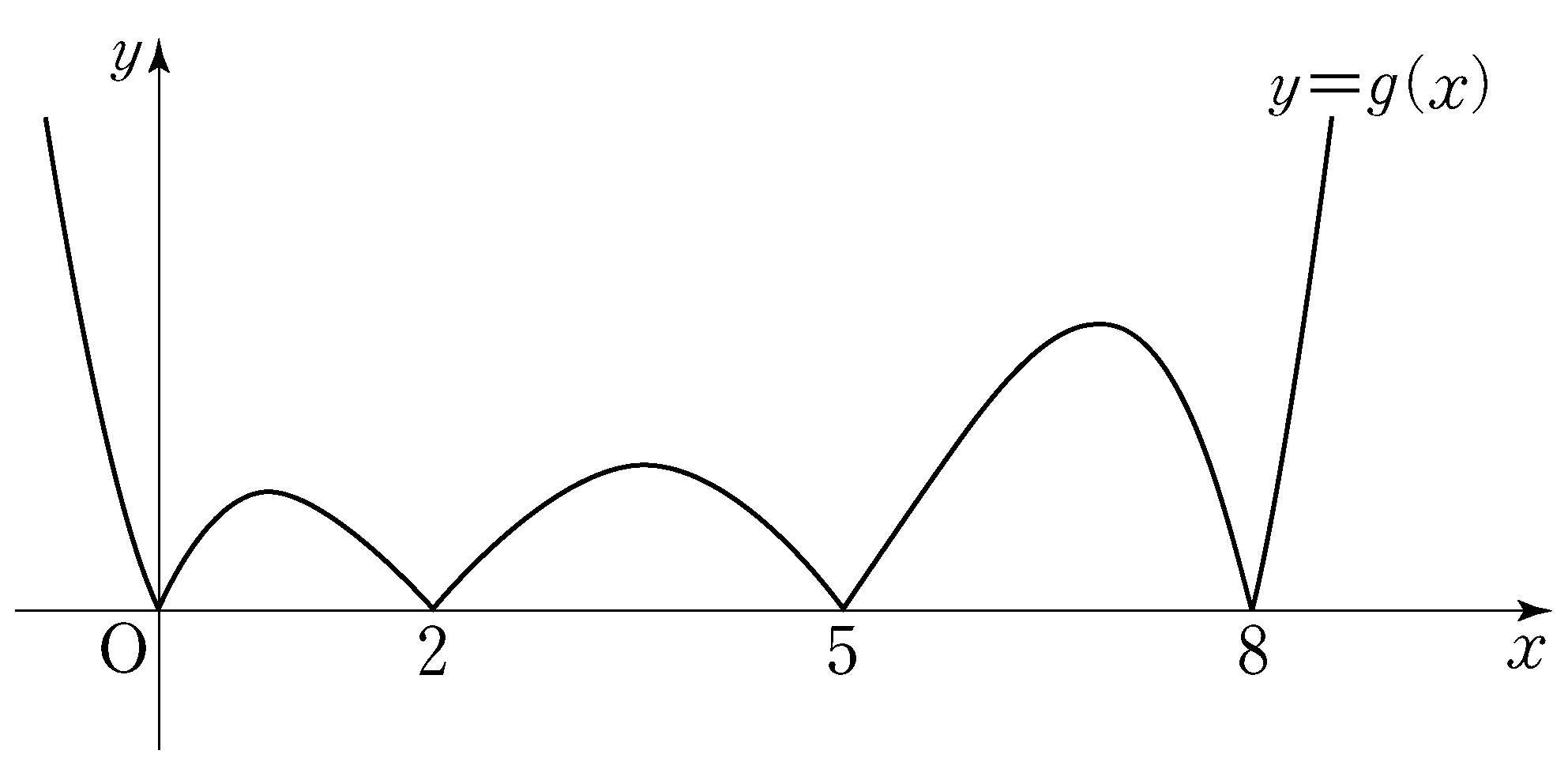
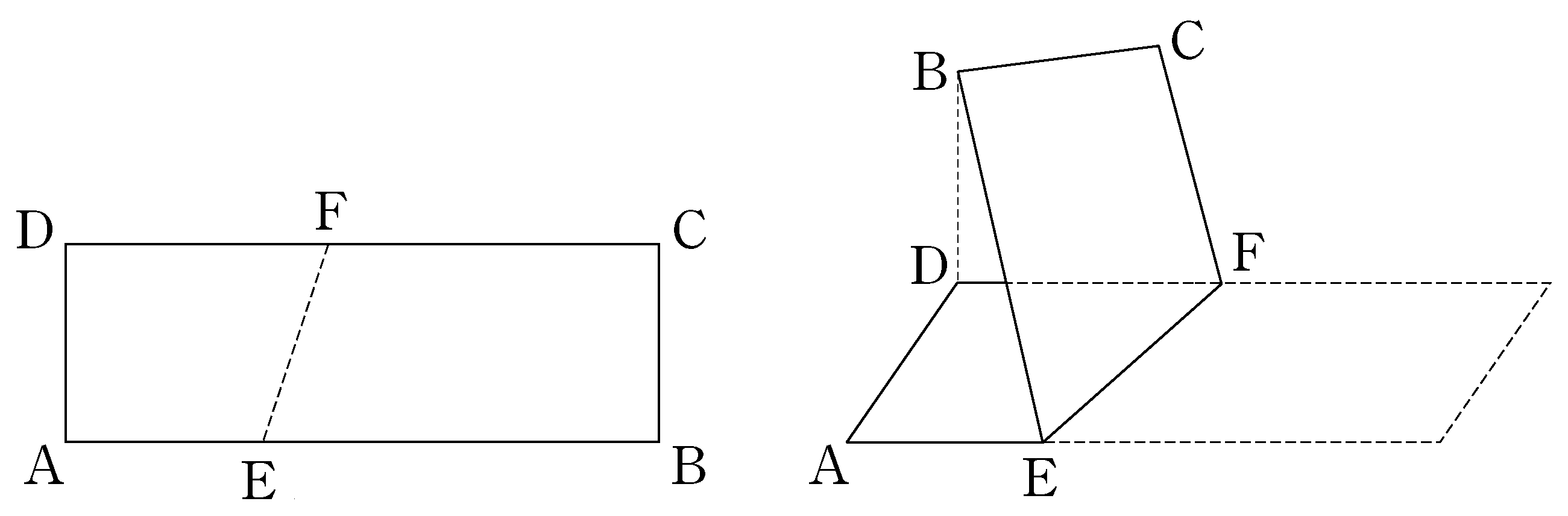
- \(10\)
- \(9\)
- \(8\)
- \(7\)
- \(6\)
Mathematics (Type Ga)
- \(26\)
- \(24\)
- \(22\)
- \(20\)
- \(18\)
- \(68\)
- \(77\)
- \(86\)
- \(95\)
- \(104\)
\(T = T_0 + k \log(8t + 1)\) (※ \(k\) is a constant.)
Consider a room with an initial temperature of \(20\)℃ on fire.
The temperature of this room \(\dfrac{9}{8}\) minutes after the fire was \(365\)℃,
and the temperature of this room \(a\) minutes after the fire was \(710\)℃.
What is the value of \(a\)? [3 points]
- \(\dfrac{99}{8}\)
- \(\dfrac{109}{8}\)
- \(\dfrac{119}{8}\)
- \(\dfrac{129}{8}\)
- \(\dfrac{139}{8}\)
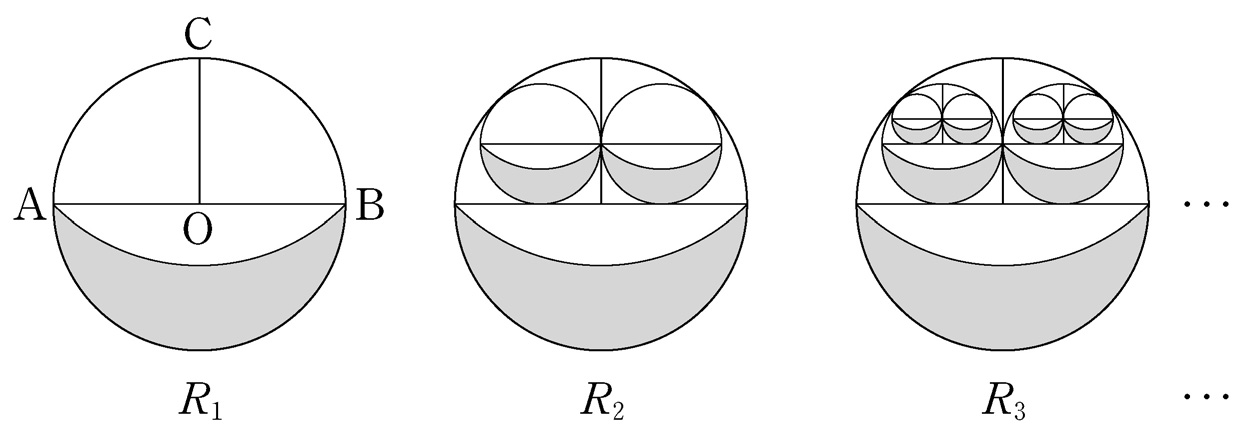
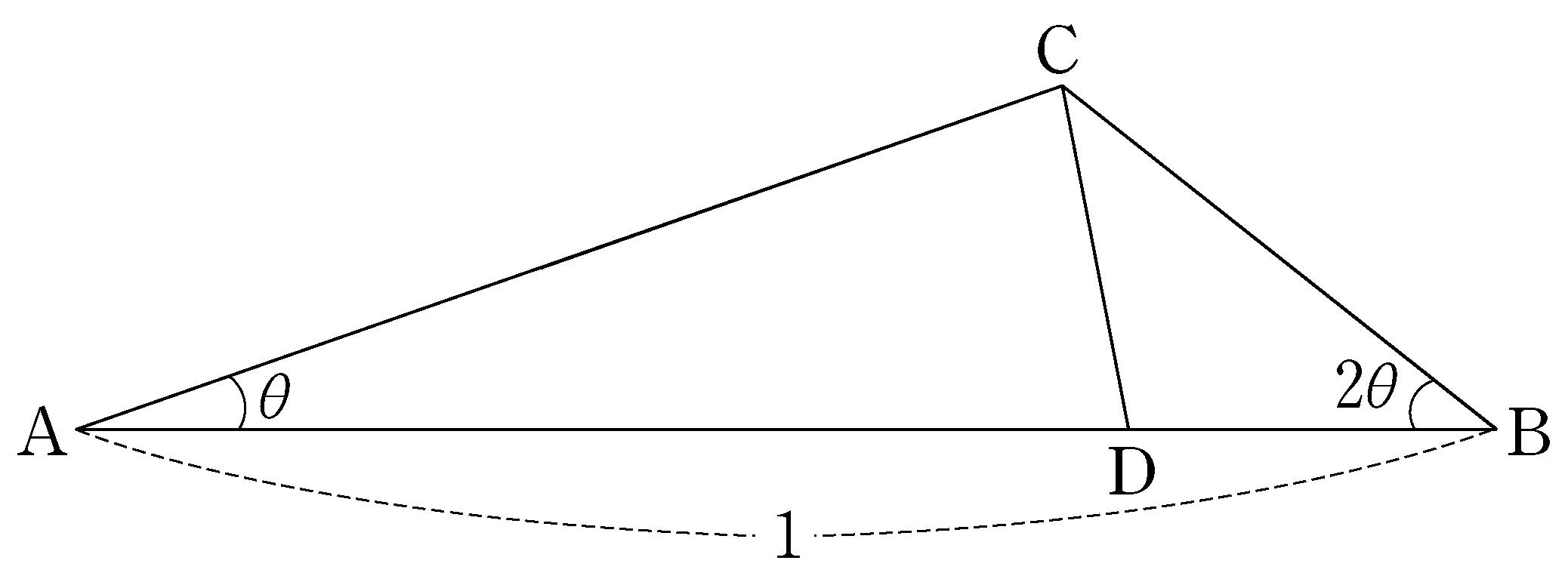
 shape outside this circle inside circle \(\mathrm{O}\).
shape outside this circle inside circle \(\mathrm{O}\).