\(a_{n+1}=n\cdot 2^n + \displaystyle\sum_{k\;\!=\;\!1}^{n}\dfrac{a_k}{k} \;(n\geq 1)\).
The following is a process computing the general term
\(a_n\).
From the given equation we have
\(a_n = (n-1) \cdot 2^{n-1} + \displaystyle\sum_{k\;\!=\;\!1}^{n-1} \dfrac{a_k}{k} \;(n\geq 2)\).
Thus for all integers \(n \geq 2\),
\(a_{n+1} - a_n = \fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)} + \dfrac{a_n}{n}\).
Therefore
\(a_{n+1} = \dfrac{(n+1)a_n}{n} + \fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)}\).
Let \(b_n = \dfrac{a_n}{n}\). Then
\(b_{n+1} = b_n + \dfrac{\fbox{\(\;(\alpha)\;\)}}{n+1} \;(n \geq 2)\)
and \(b_2 = 3\). So
\(b_n = \fbox{\(\;(\beta)\;\)} \;(n \geq 2)\).
Therefore
\(a_n = \begin{cases}
4 &\; (n = 1) \\
n \times \left(\fbox{\(\;(\beta)\;\)}\right) &\; (n \geq 2)
\end{cases}\).
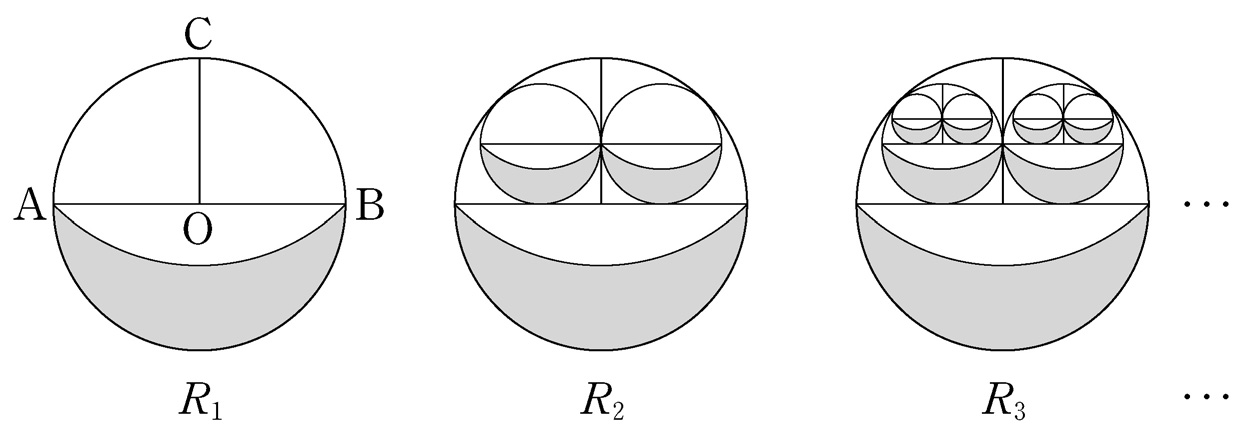
 shape outside this circle inside circle \(\mathrm{O}\).
shape outside this circle inside circle \(\mathrm{O}\).