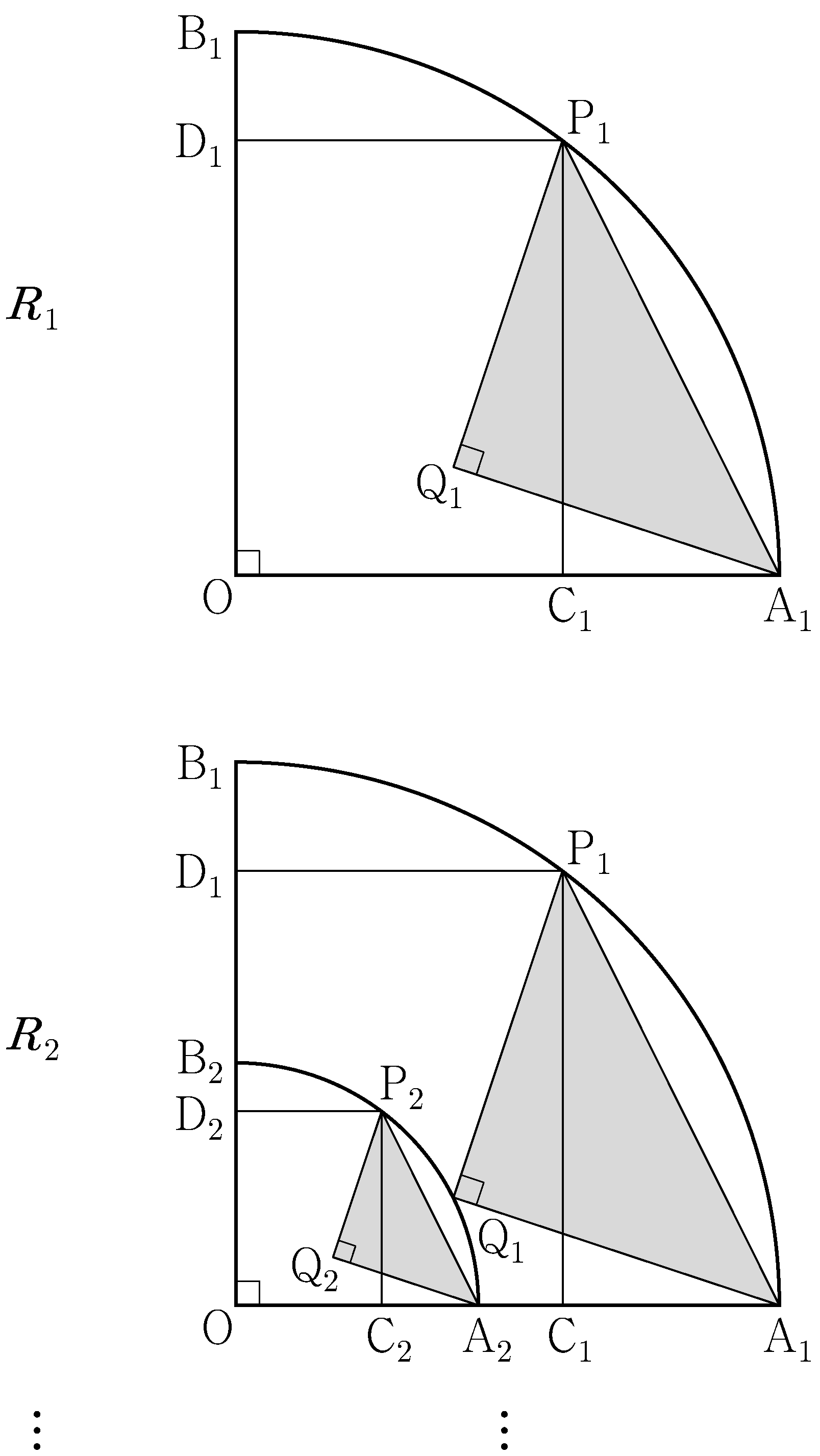
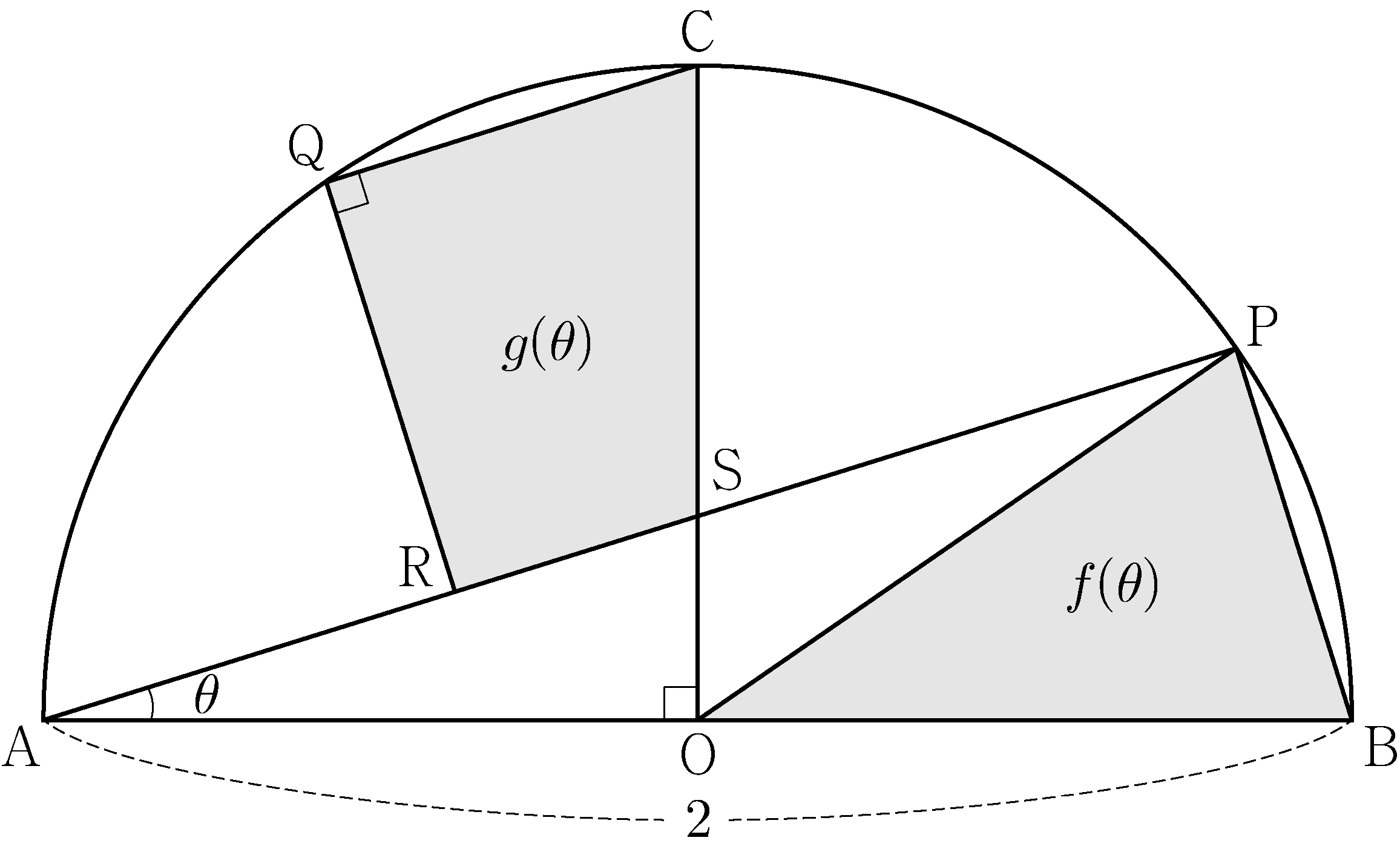
- \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
- \(1\)
- \(2\)
- \(4\)
Mathematics
- \(-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
- \(-1\)
- \(-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
- \(-2\)
- \(-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
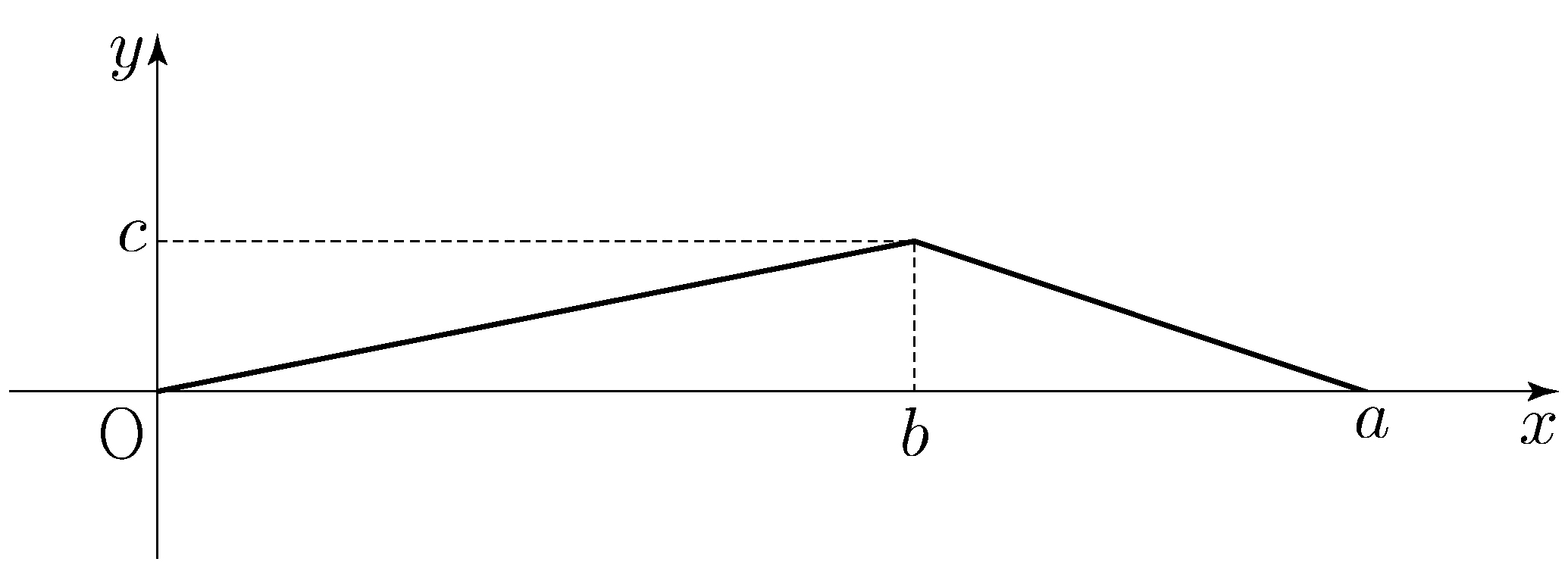
\(f(x)=a=\sqrt{3}\tan 2x\)
has a maximum value of \(7\) and a minimum value of \(3\). What is the
value of \(a\times b\)? (※ \(a\) and \(b\) are constants.)
[4 points]
- \(\dfrac{\pi}{2}\)
- \(\dfrac{5\pi}{12}\)
- \(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\)
- \(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{\pi}{6}\)
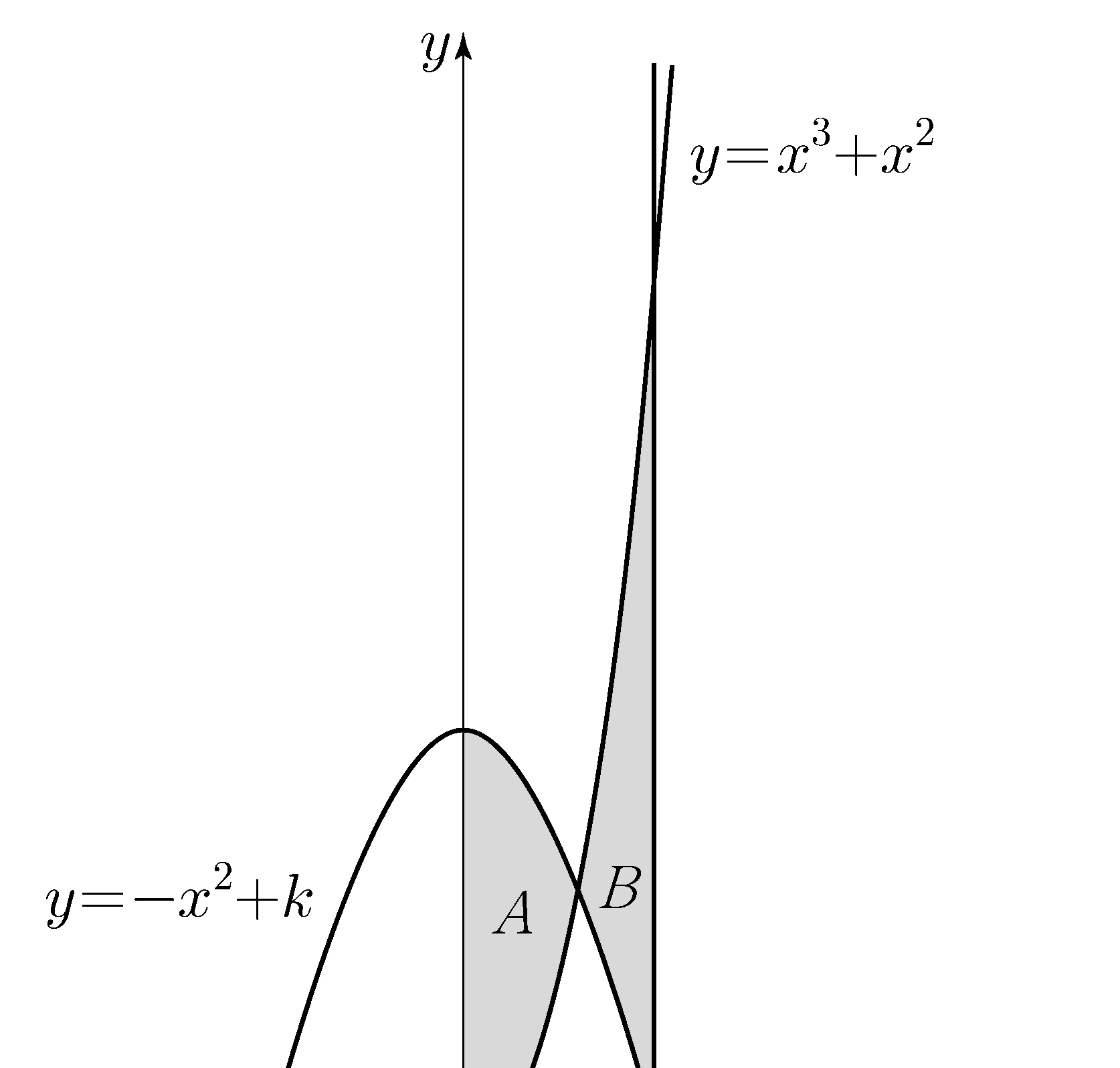
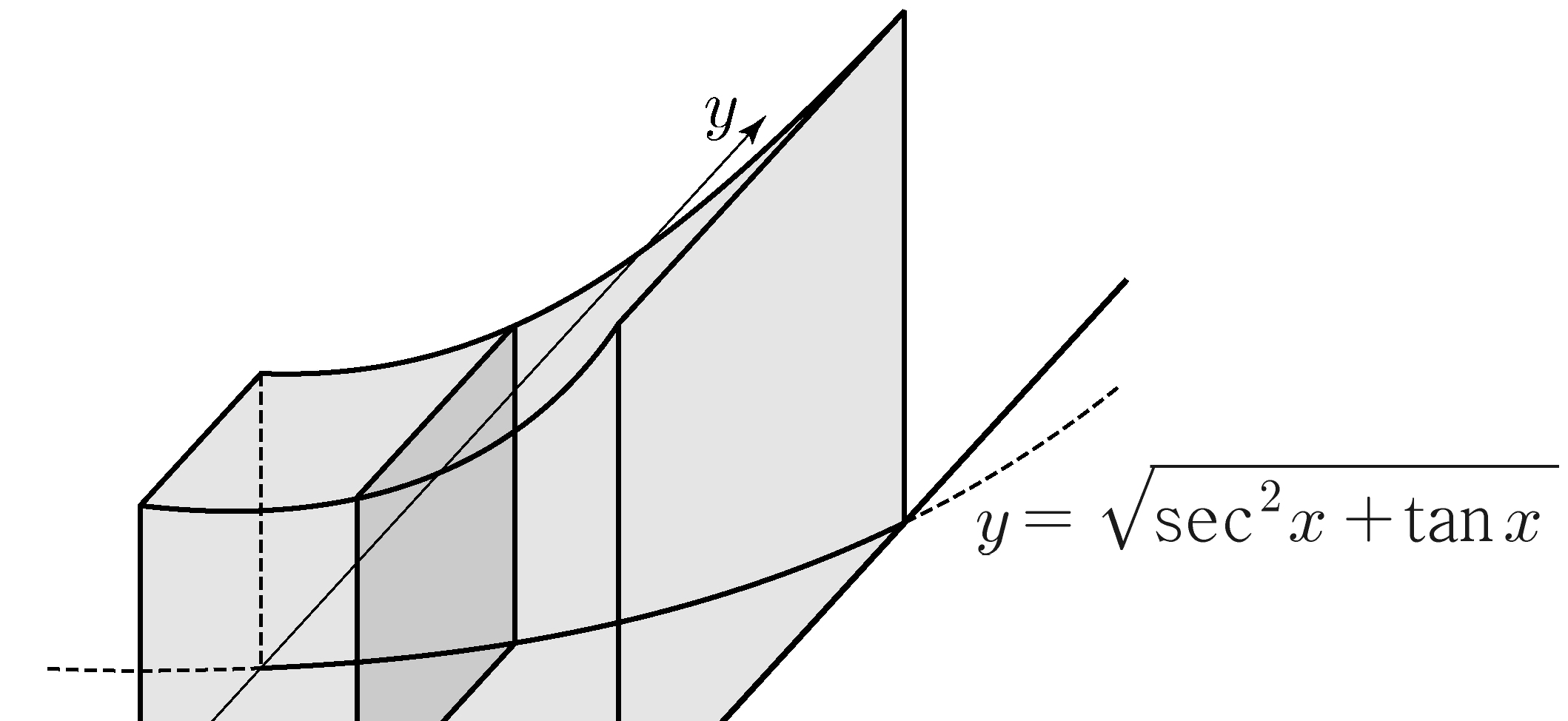
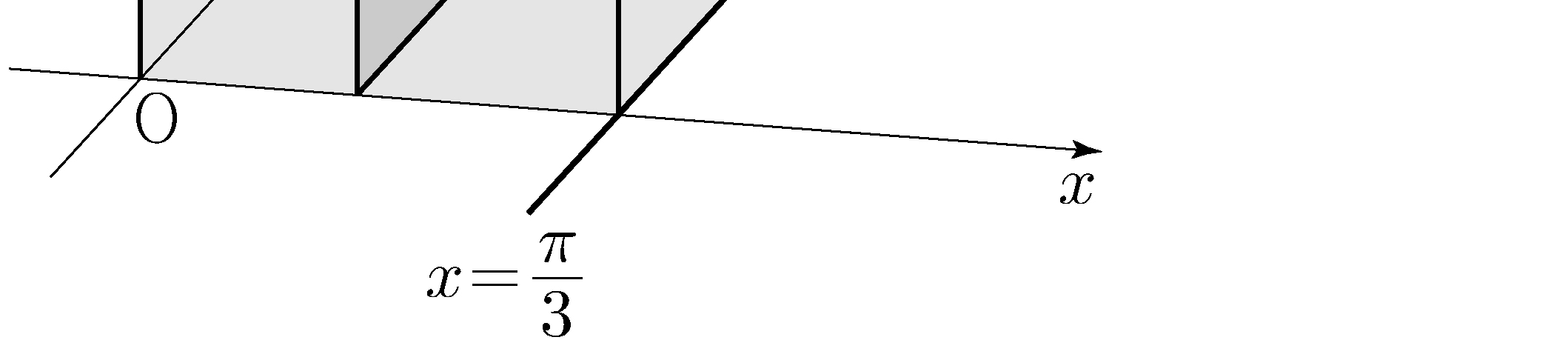
\(y\)-axis and two curves \(y=x^3+x^2\) and \(y=-x^2+k\). Let \(B\) be the area of the region enclosed by the line \(x=2\) and two curves \(y=x^3+x^2\) and \(y=-x^2+k\).
If \(A=B\), what is the value of the constant \(k\)?
(※ \(4<k<5\)) [4 points]
- \(\dfrac{25}{6}\)
- \(\dfrac{13}{3}\)
- \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
- \(\dfrac{14}{3}\)
- \(\dfrac{29}{6}\)