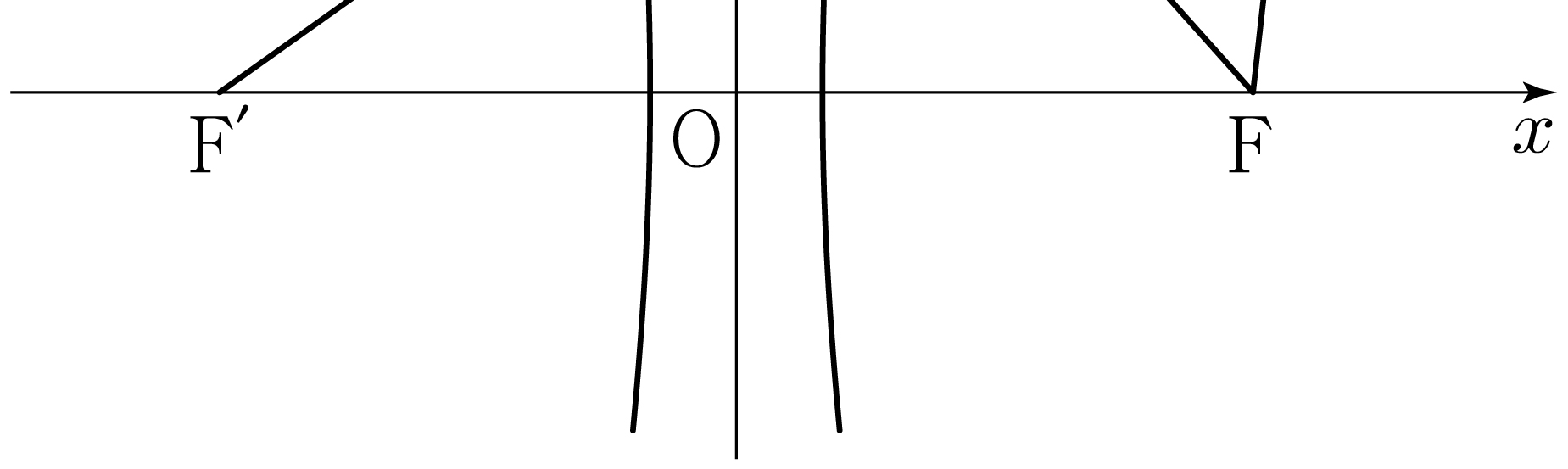
- \(1\)
- \(2\)
- \(3\)
- \(4\)
- \(5\)
Mathematics
\(f(1)=f(2)=0\,\) and \(\,f'(0) = -7\).
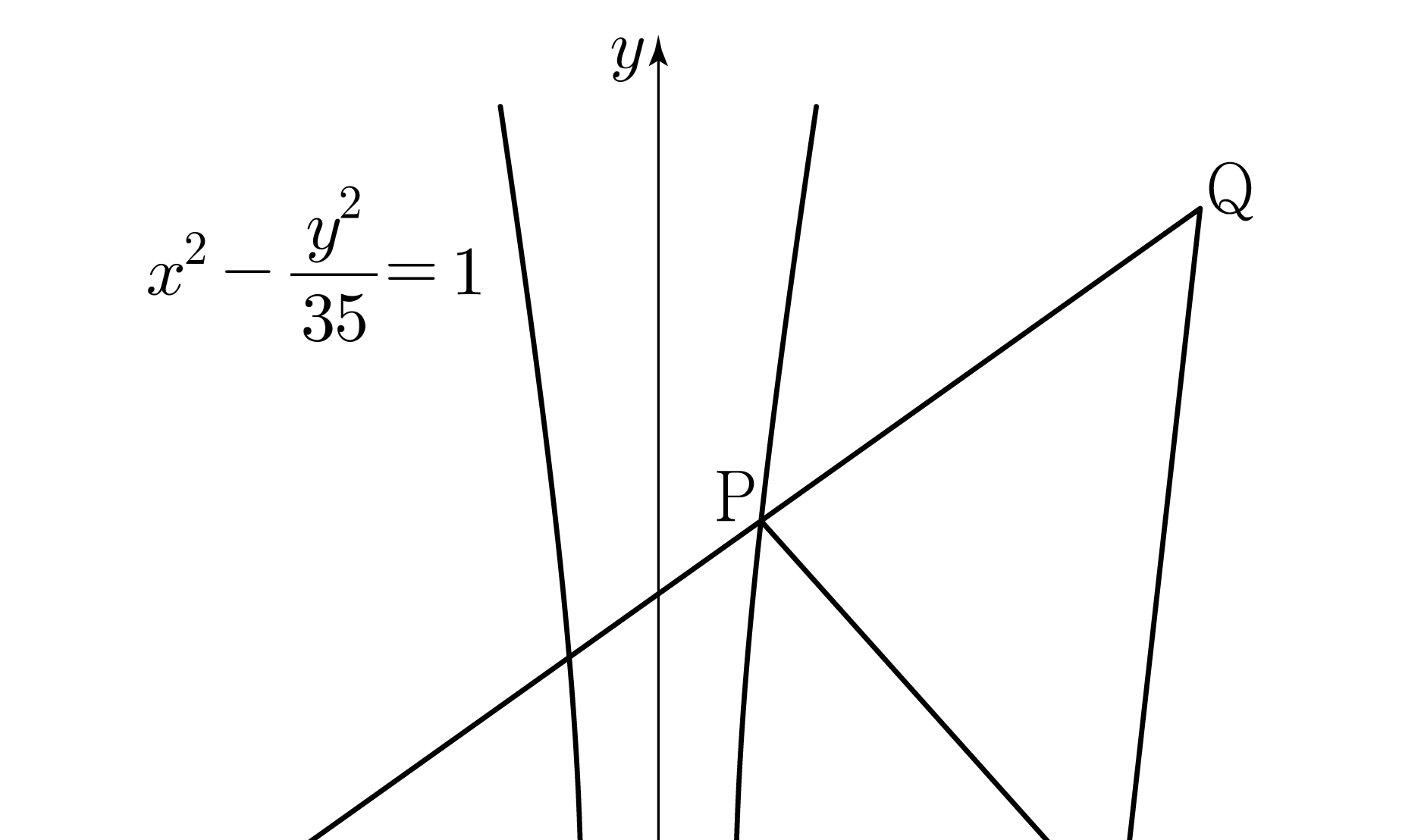
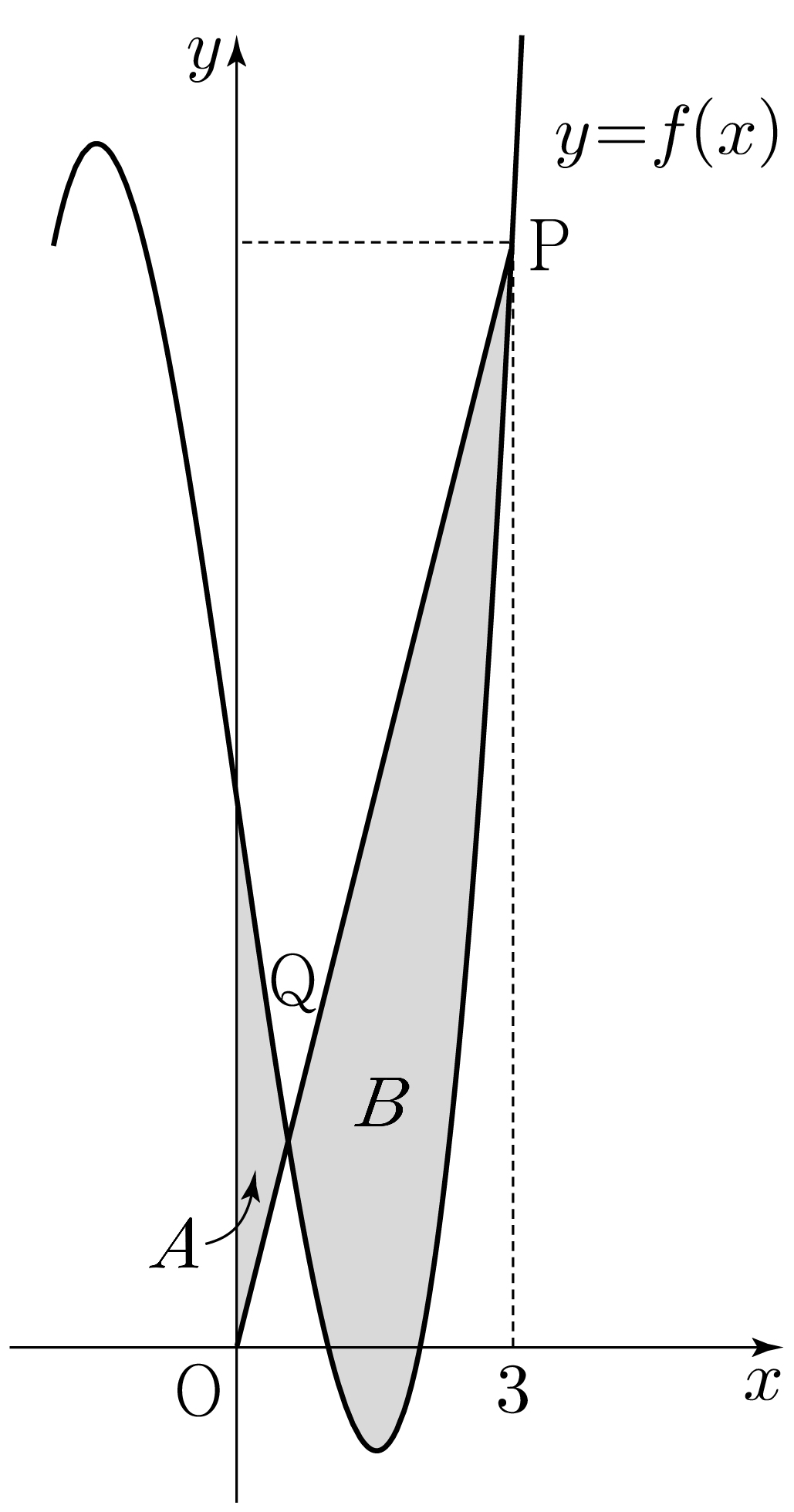
For the origin \(\mathrm{O}\) and point \(\mathrm{P}(3, f(3))\), let
\(\mathrm{Q}\) be the point where the line segment \(\mathrm{OP}\)
meets the curve \(y=f(x)\). (\(\mathrm{Q} \ne \mathrm{P}\))
Let \(A\) be the area of the region enclosed by the curve \(y=f(x)\), the \(y\)-axis, and the line segment \(\mathrm{OQ}\). Let \(B\) be the area of the region enclosed by the curve \(y=f(x)\) and the line segment \(\mathrm{PQ}\). What is the value of \(B-A\)? [4 points]
- \(\dfrac{37}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{39}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{41}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{43}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{45}{4}\)
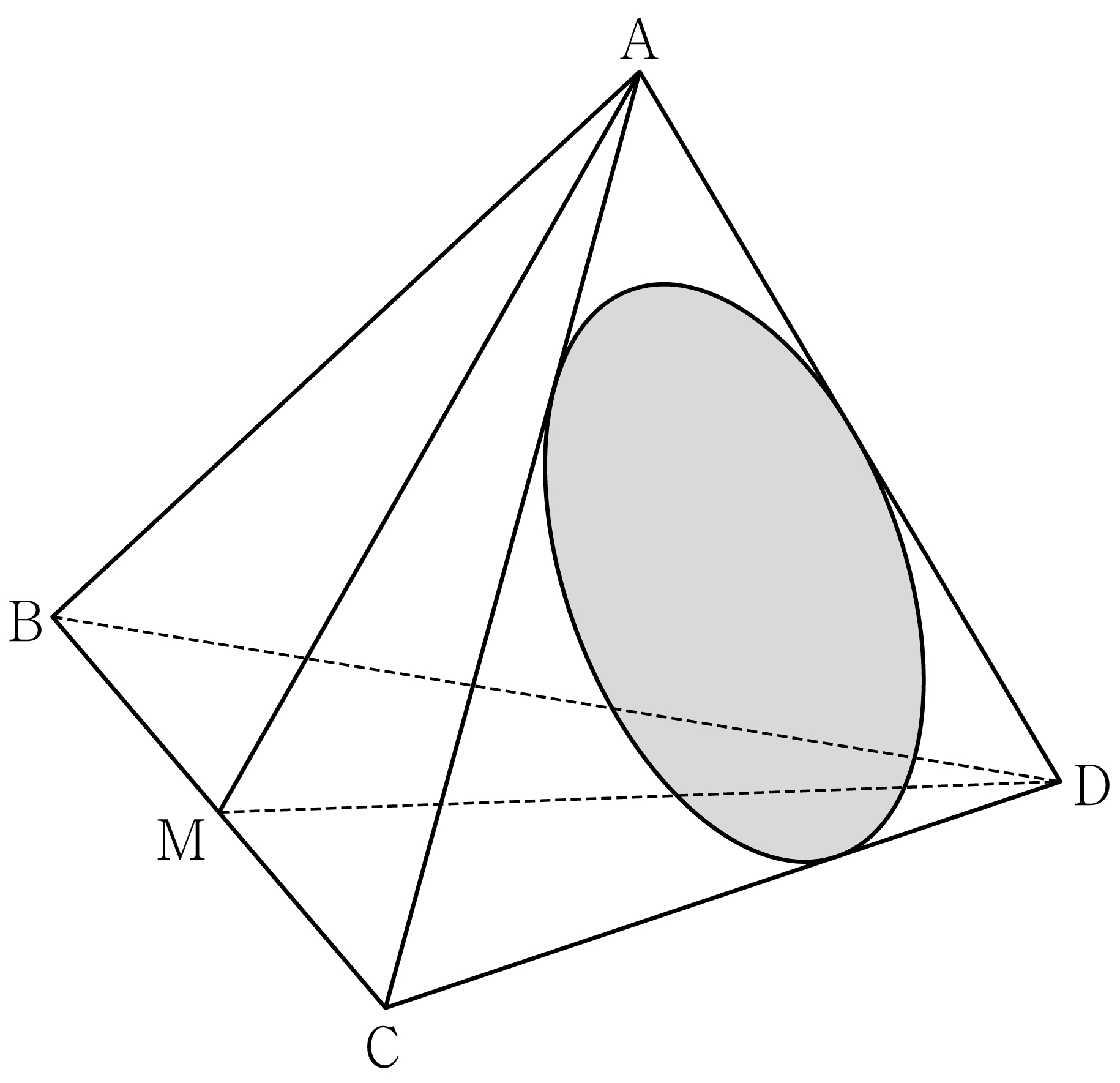
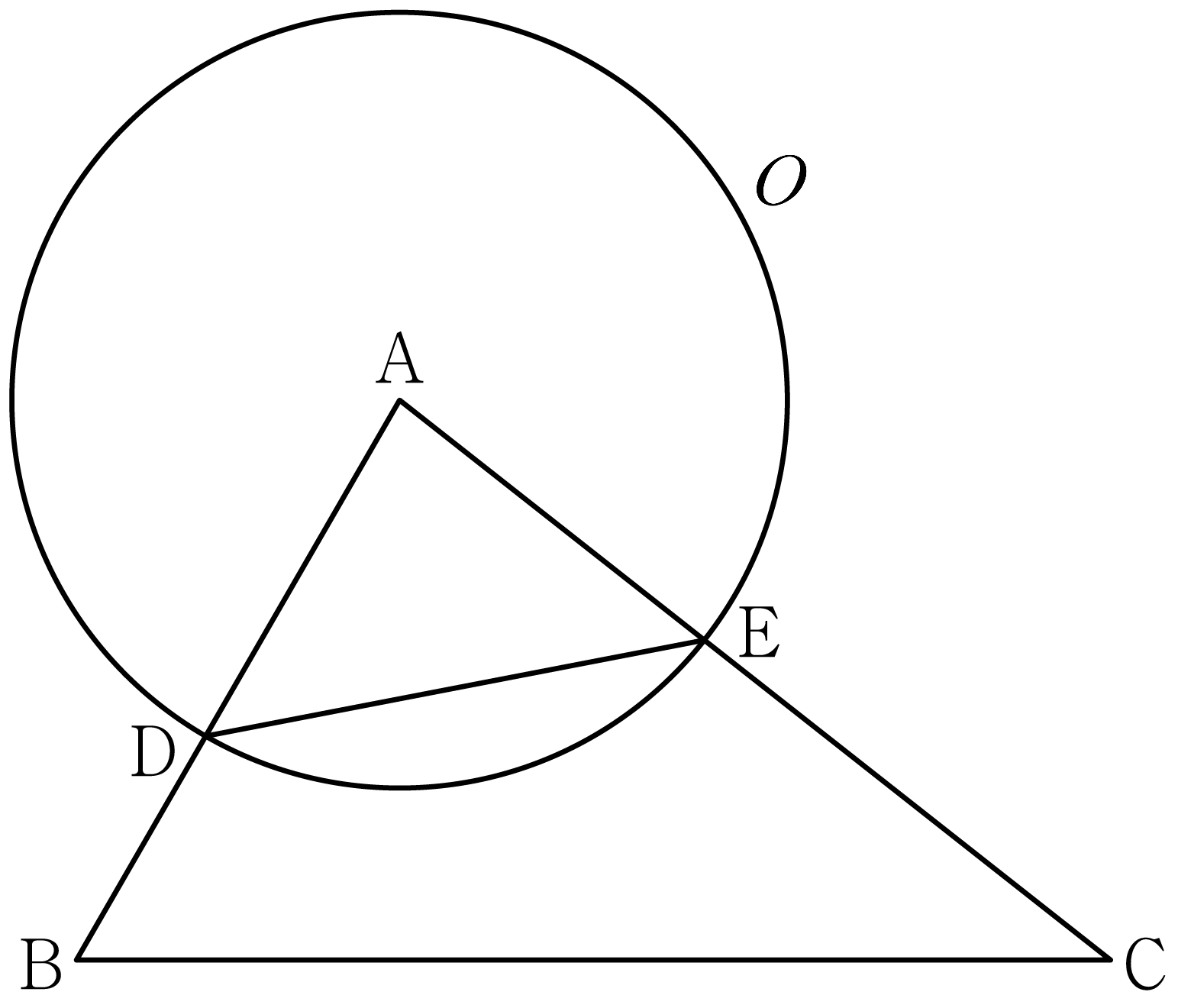
Suppose that \(\sin A : \sin C = 8:5\), and the ratio between the areas of triangle \(\mathrm{ADE}\) and \(\mathrm{ABC}\) is \(9:35\). Suppose that the radius of the circumcircle of triangle \(\mathrm{ABC}\) is \(7\). For all points \(\mathrm{P}\) on circle \(O\), what is the maximum area of triangle \(\mathrm{PBC}\)?
(※ \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}} < \overline{\mathrm{AC}}\)) [4 points]
- \(18+15\sqrt{3}\)
- \(24+20\sqrt{3}\)
- \(30+25\sqrt{3}\)
- \(36+30\sqrt{3}\)
- \(42+35\sqrt{3}\)